Kaspersky Labs has raised a red flag against a new form of phishing emails. These emails use HTML file attachments to phish their targets. Although such emails started spiking in 2019, this technique has become a common form of phishing in 2022. Between January and April, Kaspersky detected more than 2 million phishing emails of this type.
Generally, phishing uses fake web pages and email attachments to trick their victims. To counter such attacks, security software scans incoming emails and blocks those with suspicious content. But, with this new technique, such emails can evade detection by security software.
What is a Phishing Email?
A phishing email is a cyber attack that relies on deception to steal confidential information from users and organizations. Phishing victims are tricked into disclosing information that should be kept private. When a phishing email arrives, recipients have no reason to doubt the request. They believe that the party requesting the information – often posing as a familiar platform, a trusted vendor, colleague, or boss – is who they say they are. With the best intentions, phishing email victims respond without a second thought.
In phishing emails, cybercriminals often ask for the following information:
- Date of birth
- Social security number
- Phone number
- Home address
- Credit card details
- Login details
- Password (or other information needed to reset your password)
Cybercriminals then use this information to impersonate you and apply for credit cards or loans, open bank accounts, and commit other fraudulent acts.
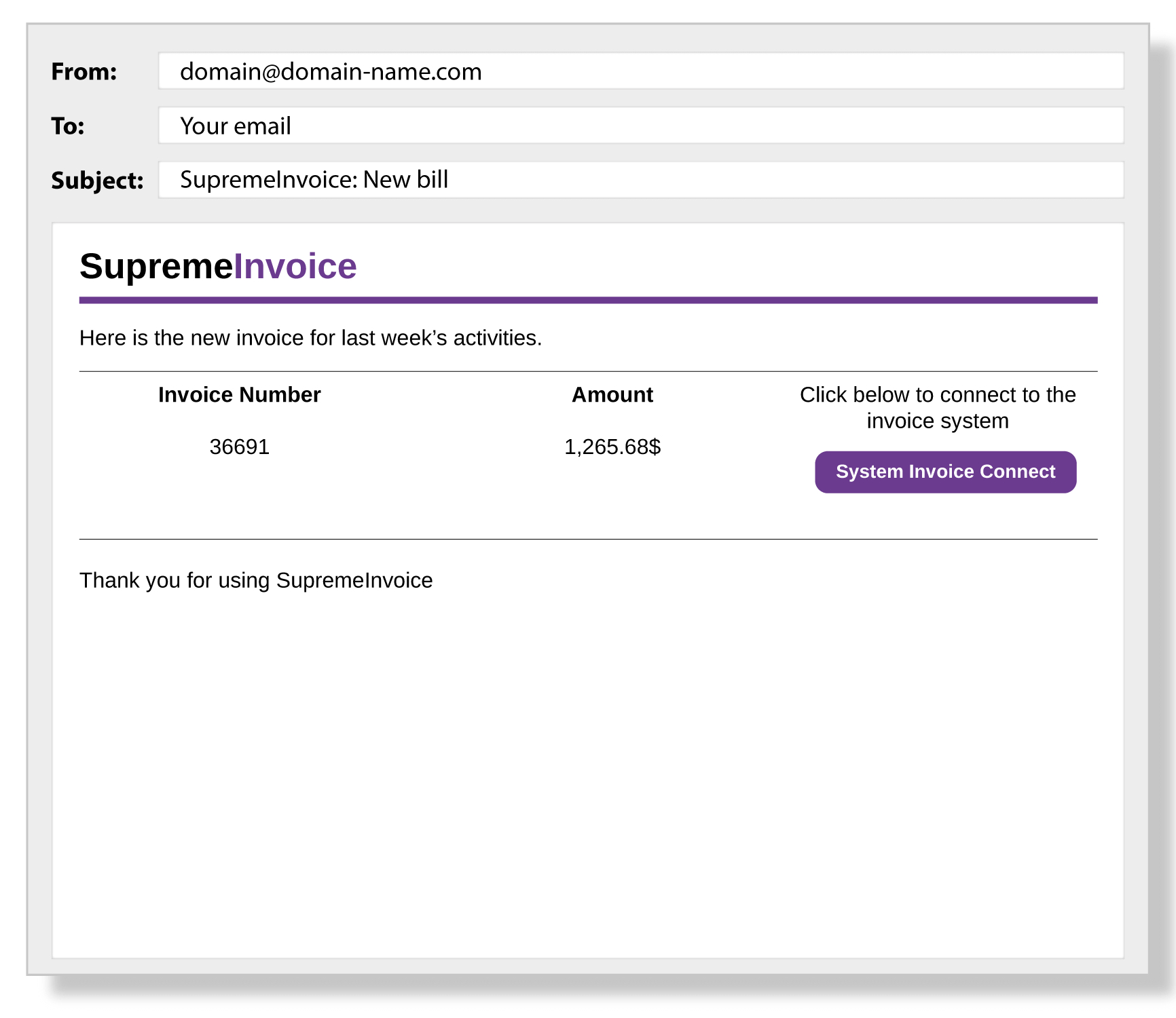
How to recognize a phishing email
Mismatched Email Addresses: The displayed name might look legitimate, but the actual email address may be a jumbled mix of characters or slightly altered from the official domain.
Suspicious Links: Hover over any links without clicking on them. This will display the link’s destination URL. If it looks suspicious or doesn’t match the purported sender’s website, it’s likely a phishing attempt.
Poor Grammar and Spelling: While not always a definite sign, many phishing emails contain misspellings, poor grammar, or awkward phrasing.
Generic Greetings: Phishing emails often use generic greetings like “Dear customer” instead of your actual name.
Request for Personal Information: Legitimate companies will never request sensitive information, like passwords or social security numbers, via email.
Unsolicited Attachments: Be wary of unexpected attachments. They might contain malware.
Urgent or Threatening Language: Phishers often use urgency to their advantage. Phrases like “urgent action required” or “your account will be suspended” can be signs of a phishing attempt.
Requests for Money: Any unexpected request for money, especially via wire transfer or an untraceable method, should be an immediate red flag.
Too Good To Be True: Offers that seem too good to be true often are. Be skeptical of any email offering rewards, cash, or gifts out of the blue.
Mismatched URLs: If the email claims to be from a known organization but the URL is different from the organization’s known URL, it’s a red flag.
Unusual Sender: If you receive an email from someone you haven’t communicated with before or don’t expect to hear from, be cautious.
Altered Logo or Branding: Look for slightly altered logos or off-brand coloring. The phishers might recreate logos, but sometimes small inconsistencies can give them away.
No Contact Information: Legitimate businesses will have their contact information available. If it’s missing, that’s suspicious.
Check the Signature: Generic signatures like “Support Team” or “Customer Service” without specific contact details can be a sign of a phishing email.
8 Types of Email Phishing
Deceptive Phishing: This is the most common type. Attackers impersonate a legitimate company to steal personal information or login credentials. They often use threats to create a sense of urgency, like “Your account will be closed if you don’t respond.”
Spear Phishing: Targeted at specific individuals or companies. Attackers often gather detailed information about their victims to make the scam more believable.
CEO Fraud / Business Email Compromise (BEC): A type of spear phishing where attackers pretend to be a high-ranking executive or company CEO. They’ll typically request an urgent wire transfer or sensitive information.
Pharming: Even though this isn’t strictly an email-based attack, it’s closely related. In pharming attacks, cybercriminals redirect users from a legitimate site to a fake one. The transition is often seamless, and users might not notice they’ve been redirected.
Whaling: This is a more targeted version of spear phishing where high-profile individuals like C-level executives, politicians, or celebrities are the primary targets.
Vishing: While this is mainly phone-based, it’s worth mentioning because phishing emails can request the victim to call a particular number. The goal is to extract personal information during the call.
Dropbox Phishing: Attackers send notifications from popular cloud storage providers like Dropbox, urging users to click on a link. Once they do, they’ll be asked to enter their login credentials.
Google Doc Phishing: This attack became famous in 2017 when a malicious actor sent a deceptive invite to access a Google Doc. When clicked, it led users to a page that asked for their Google login details.
Examples of Phishing Emails in Everyday Scenarios
Highlighted below are typical phishing email scenarios:
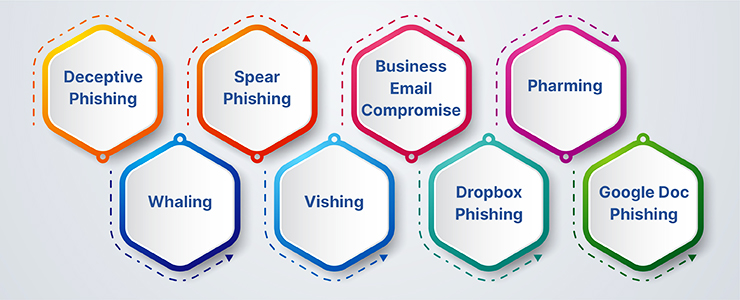
Account Verification Alert: An email mimics PayPal, alerting the receiver about potential account breaches. The recipient is urged to validate their credit card on a fraudulent PayPal site, where the data is captured for illegal activities.
Credit Card Security Alert: Post a recent Apple purchase, an email, masquerading as Apple’s support, warns about possible credit card breaches and asks for card validation.
Urgent Funds Transfer: An email, seemingly from the company’s traveling CEO, requests an emergency funds transfer to a foreign associate. The receiver, believing in aiding the company, promptly acts on it.
Social Media Link: A friend request on Facebook from a seemingly mutual friend leads to a message containing a malicious video link that, once clicked, deploys malware.
Google Docs Authentication Alert: An email prompts the user to verify their Google Docs login on a counterfeit page. The email might be from a deceptive address like accountupdate@google.org.com.
IT Support Software Update: An official-looking email, ostensibly from the company’s IT department, suggests downloading new messaging software. The download link, however, deploys ransomware on the network.
Phishing Techniques Overview
Phishing schemes aren’t just about sending deceptive emails and hoping recipients fall for them. There are advanced methods cybercriminals employ to deceive their targets, such as:
URL Misrepresentation. By using JavaScript, cybercriminals can overlay a genuine URL image on a browser’s address bar. The true URL becomes evident when you hover over a link within the email. Attackers can also modify this using JavaScript.
URL Camouflaging. Also known as URL hiding, it’s a prevalent strategy in phishing attacks. Here, the displayed URL appears authentic, but it leads users to a malevolent site.
Use of URL Condensers. By taking advantage of services like Bitly, attackers can conceal the real destination of a link. For unsuspecting victims, it’s tough to determine whether the abbreviated URL leads to a trustworthy or harmful site.
Character Deception in URLs. Attackers craft URLs using characters that closely resemble those in trusted domain names. This way, they can establish fake sites that appear authentic to the untrained eye.
Image-based Messages. By converting textual content into images, attackers can sometimes dodge phishing detection tools. Since many security solutions search for specific text patterns found in phishing attempts, converting the text to an image can avoid these scans.
Hidden Redirects. In this technique, victims believe they’re giving personal information to a trusted entity. But in reality, they’re first directed to a malicious intermediary site that captures their details, only then to be sent to the genuine site.
Enhanced Chatbots. Leveraging AI, cybercriminals can perfect the language used in phishing messages. AI-driven chatbots can refine the text, eliminating the grammar and spelling mistakes usually present in phishing content, and making detection tougher.
Voice Mimicking with AI. Cybercriminals can harness AI to replicate someone’s voice, making it sound as if a known individual or authority figure is speaking. To achieve this realistic effect, they only need a brief audio snippet from the intended impersonated party.
How Phishing Emails Can Bypass Your Email Security Using HTML Smuggling
This is how it works. The emails contain an HTML attachment or a zipped file. When the user opens the attachment, it runs a malicious script. Threat actors are using these attachments to redirect users to malicious websites and display spoofed login forms. These attachments are being used for installing malware over corporate networks.
Unfortunately, as HTML is not malicious, mail security tools fail to mark the messages as phishing attempts. Thus, increasing the number of phishing emails that reach victims’ inboxes.
In addition, security researchers have found signs of HTML smuggling as well.
What to Do if You’ve Been Phished
If you have already responded to a phishing email, follow these steps to protect you and your business:
- Change your passwords immediately, starting with your most sensitive accounts.
- Alert your bank and credit card companies.
- Monitor your accounts for suspicious activity.
- Report the phishing attempt to the platform or service impersonated.
- Update and run antivirus software.
- Be vigilant and educate yourself about common phishing signs.